📍 GPT-Powered Parser
For more advanced LLM-powered parsing, please check out our second tool, Airparser (see the "Advanced GPT-Powered Parsing" section of this article).
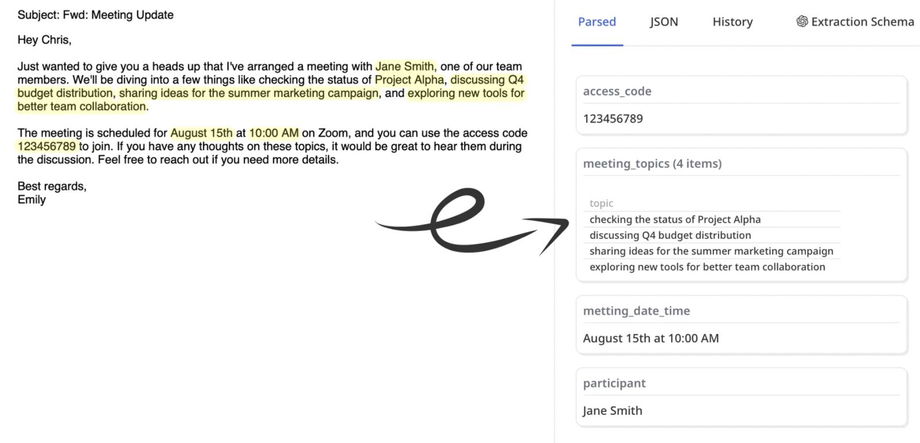
The GPT-powered parser allows you to extract structured data from emails, PDFs, and files using a text prompt (similar to ChatGPT).
The advantage is that there is no need to create parsing templates or complex parsing rules. Simply specify the desired fields to extract from the document. Feel free to write your prompt in a conversational tone, as if you were talking to a person, but be specific in your description.
Some use cases for the parser are:
Parsing complex PDF files (candidates CVs, reports, ...).
Parsing emails and tables (SEO reports, Amazon order emails, ...).
Parsing human-written emails and texts without a fixed layout that the template-based parser is unable to process (flight details, ...).
Extract contact details from email signatures (the email signature parser is also available using the template-based parser).
The prompt is defined at the mailbox level, meaning it is the same for all the documents in that mailbox.
Supported formats: Emails, PDFs, HTML, TXT, DOCX, XML, MD, and JSON.
Parsing PDF Files Using the GPT-powered Parser
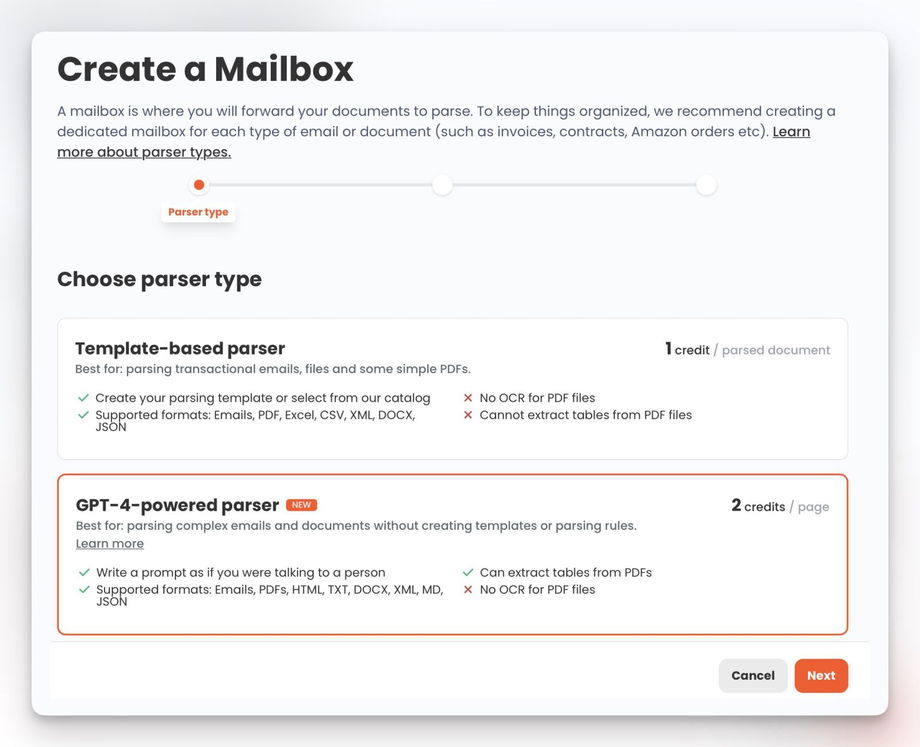
1. Create a new inbox and select the GPT-powered parser.
2. Upload a sample CV PDF file.
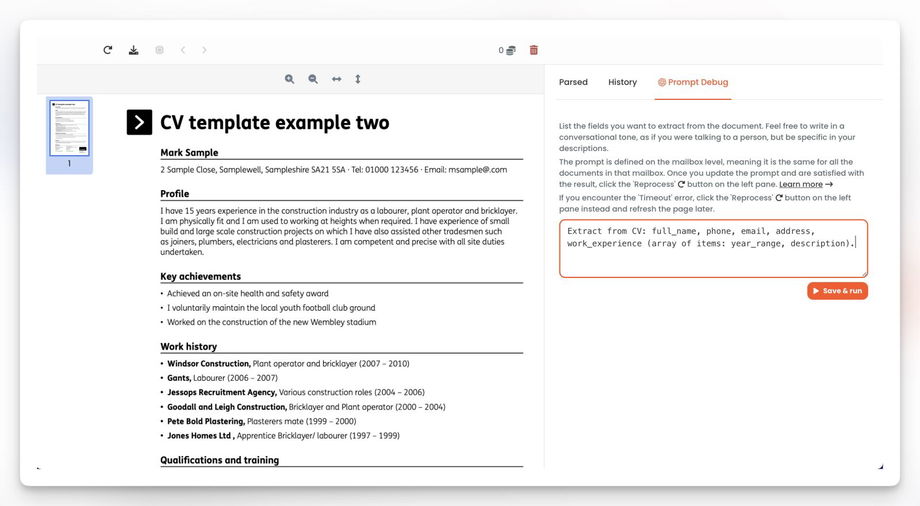
3. Open the "Prompt Debug" tab and write a prompt. In our case, we will write: Extract from CV: full_name, phone, email, address, work_experience (array of items: year_range, description).
4. Click the "Save & run" button and wait for the parsed data. Note that this is a preview of the parsed data and it's not saved in the document's result (Parsed/JSON tabs).
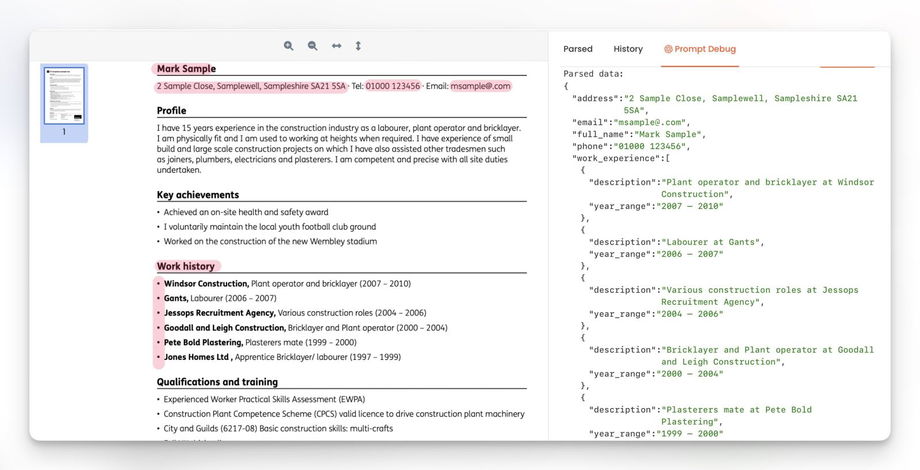
5. If the parsed result looks correct, you can finally parse your CV by clicking the "Reprocess" button.
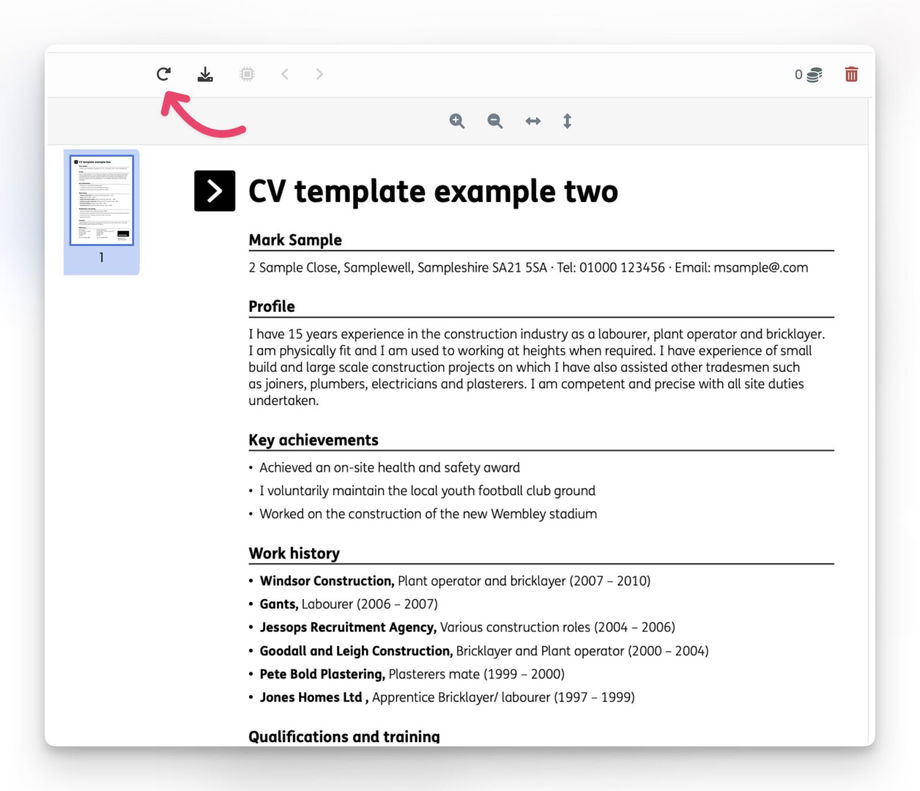
All the incoming PDF files in that mailbox will be automatically processed using the same prompt.
If you update the prompt, previously parsed documents will not be automatically reprocessed. You will need to manually click the 'Reprocess' (or 'Reprocess All') button.
Tips for Writing Effective Prompts
When using the GPT-powered parser, the way you write your prompt has a big impact on the accuracy and consistency of the extracted data. Below are some best practices.
1. List all fields explicitly
Always tell the parser exactly which fields you want. Avoid vague requests like “extract the invoice details”. Be precise.
✅ Good: Extract the following fields: "invoice_number", "invoice_date", "total_amount", "customer_name"
❌ Bad: Extract invoice details
2. Use lowercase with underscores for field names
To keep your data clean and machine-friendly, write field names in lowercase with underscores (snake_case). This ensures consistent naming across documents.
✅ Example: "invoice_number", "customer_name", "total_amount".
3. Put field names in quotes
Quoting field names makes the parser more likely to return exactly those names, without variations.
✅ Example: Extract a list of "items". Each "item" should have: "description", "quantity", "unit_price", "total_price".
This way, the parser knows exactly how to structure the list of items.
Putting it all together
Here’s a full prompt for parsing an invoice:
Extract the following fields:- "invoice_number"- "invoice_date"- "supplier_name"- "customer_name"- "total_amount"- "currency"- "items": a list where each "item" has "description", "quantity", "unit_price", "total_price"This will give you consistent, structured JSON output that works well across multiple documents.
Limitations
The GPT-powered parser doesn't currently support OCR functionality. Therefore, it is unable to parse text from images and scanned PDF files.
Data privacy note: Your data is not used to train or improve AI models.
Advanced GPT-Powered Parsing
Parsio offers a powerful yet simple GPT parser. You can enter one multiline parsing prompt.
You may consider checking our second product: Airparser (https://airparser.com), which offers a more advanced LLM-powered parser compared to Parsio.
The key distinction is that Airparser allows you to create a structured parsing schema instead of a single text prompt. It also supports OCR for scanned documents and images. Airparser is particularly effective for unstructured and human-written docs.